Introduction
Cybersecurity frameworks offer a systematic way of dealing with such risks to ensure that systems, data, and operations are protected. This article seeks to give an insight of the NIST and ISO cybersecurity frameworks and how they can be useful in managing cybersecurity risks.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
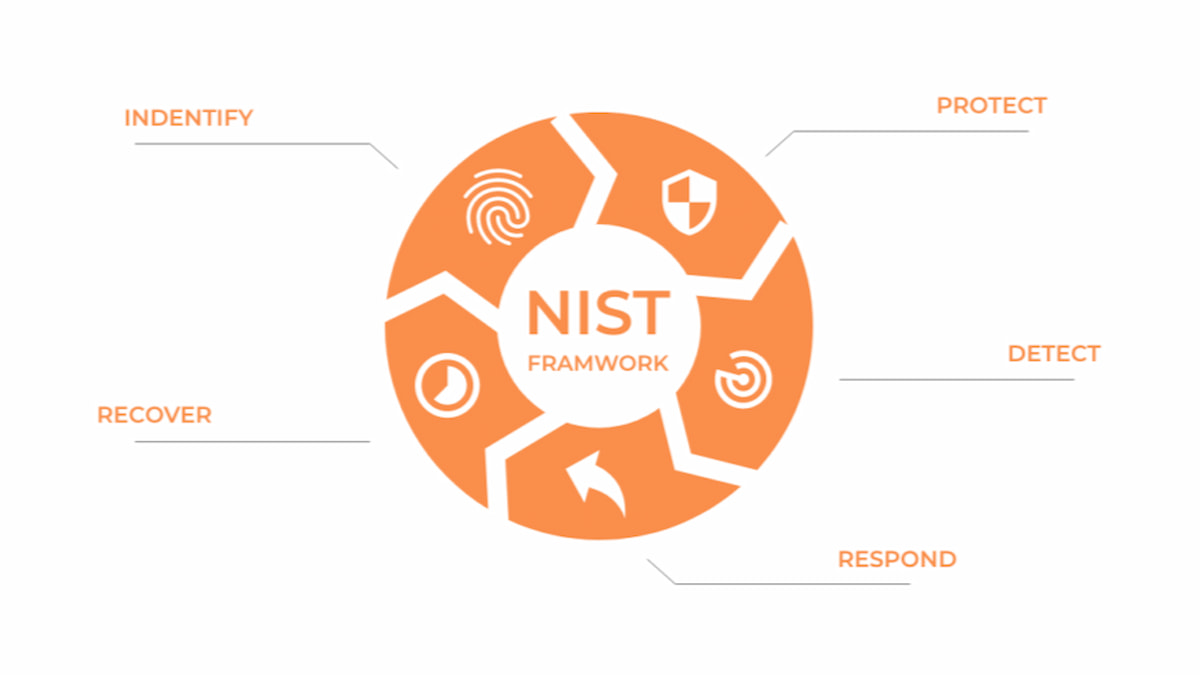
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) was designed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology as a result of rising cyber threats that threatened the country’s critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, healthcare, and financial services. After its release, it has been embraced by various organizations across the globe irrespective of their size and operation in different industries due to its flexibility and practicality in handling cyber risks.
The NIST framework is built around five core functions that provide a strategic, high-level approach to managing cybersecurity:
- Identify: The first step is to identify what has to be protected. This entails the determination of key system, asset, data and the level of risk within an organization.
- Protect: After the risks have been identified, measures have to be taken to mitigate the risks that are posed by cyber threats. This could entail deploying security measures such as controls, access management policies or even encryption.
- Detect: It is imperative that organizations have mechanisms that enable them to identify cybersecurity threats as they happen. This could include putting in place monitoring devices and also the intrusion detection systems.
- Respond: When there is a security threat, organizations require to respond appropriately. The “Respond” function provides measures to be taken in case of a cyber attack, including communication and containment measures.
- Recover: The last one is on the recovery from the security incident and using the experience gained to prevent similar occurrences in the future.
NIST Implementation Tiers
In addition to its five core functions, the NIST framework is structured into four Implementation Tiers that help organizations assess their cybersecurity maturity:
- Tier 1: Partial (cybersecurity activities are reactive and not well coordinated)
- Tier 2: Risk-Informed (some of the risk management activities are structured but not standardized)
- Tier 3: Repeatable (There are formal risk management policies that are always used).
- Tier 4: Adaptive (organizations are active and are always working on enhancing their cybersecurity standards).
Advantages of the NIST Framework
- Flexibility: NIST is intended to be scalable for organizations of all sizes and industries so that the organizations can apply the framework to their risks and circumstances.
- Risk-Based Approach: It focuses on risk management, this means that it assists organization to allocate its resources in accordance to the most important risks.
- Cross-Organizational Communication: NIST makes it easier for different teams in an organization to understand each other since they are all using the same language and structure from IT to senior management.
ISO 27001 Cybersecurity Framework
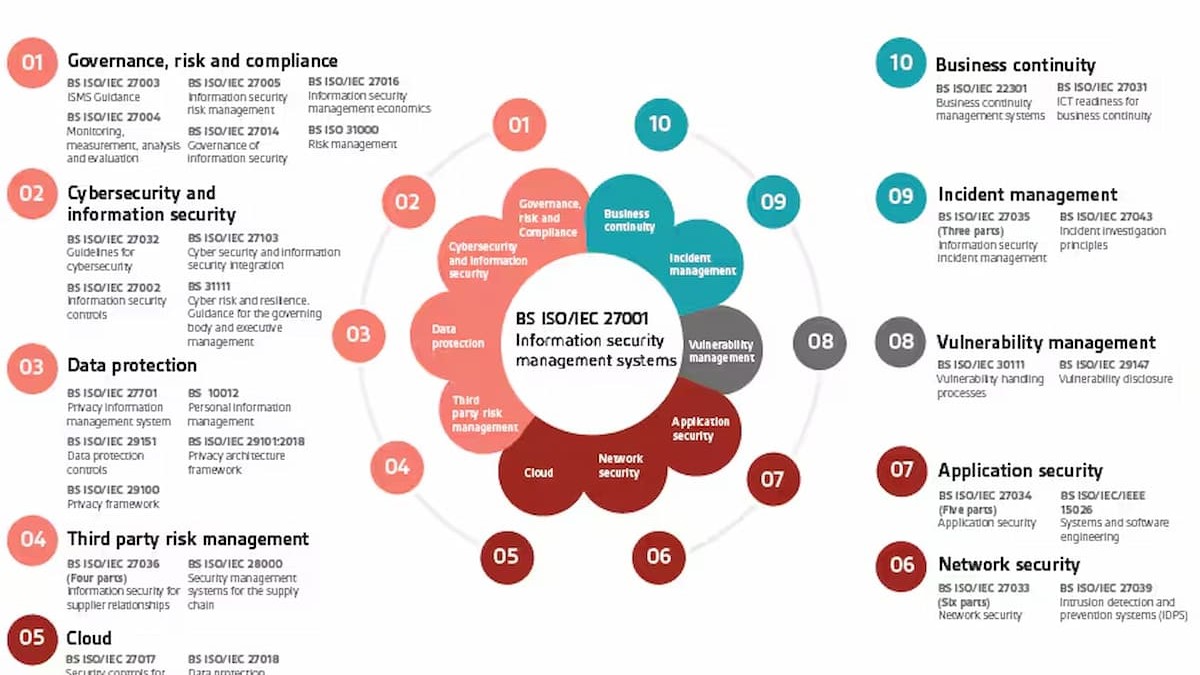
ISO 27001 is the part of the ISO/IEC 27000 series that is a set of international standards that aims at the management of information security. ISO 27001 is a standard that helps an organization to develop, implement, and maintain an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This framework is to make sure that an organization’s information is protected regardless the form it takes; data, intellectual property or client records.
ISO 27001 Certification
Another important feature of the standard is that it is possible to be certified according to ISO 27001. It is also possible for an organisation to get an external audit to ensure that it is in compliance with the standard and get a certification. This certification is well known and can be an important factor in proving the organization’s compliance to information security.
Annex A: Security Controls
ISO 27001 comprises a list of Annex A Controls that are 114 security controls grouped under 14 domains. These domains cover a wide range of security areas, including:
- Information Security Policies
- Human Resource Security
- Access Control
- Physical and Environmental Security
- Communications Security
- Supplier Relationships
Benefits of ISO 27001
- International Recognition: ISO 27001 is internationally accredited, and therefore suitable for organizations that have their operations in different countries or those that need to meet an international standard.
- Certifiable: ISO 27001 certification can be an advantage and can be used as a proof to customers and partners that the organization is serious in maintaining a good security posture.
- Comprehensive Security Management: The ISO 27001 framework covers a wide range of information security risks, including technical, process, human, third-party, and physical risks.
Conclusion
There are various factors that determine the right framework to use in an organization, some of them are; the type of business, geographical location and the level of security required. Whether an organisation chooses NIST for its flexibility or ISO 27001 for its structured, certifiable approach, organisations can increase their organisations’ resistance to cyber threats by aligning with one of these frameworks.